How to operate a drone is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding its components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore legal considerations, safety protocols, and troubleshooting techniques, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced features, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable flight experience. We’ll break down complex concepts into easily digestible steps, illustrated with clear explanations and helpful visuals. Prepare for takeoff!
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight and functionality. This section details the major components, their functions, and variations.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Drone Component Functions, How to operate a drone
A drone’s functionality relies on the coordinated work of several key components. These components work together to provide lift, stability, control, and image capture.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this sophisticated computer processes data from various sensors and controls the motors to maintain stability and execute flight commands.
- Battery: Provides the power for all drone components. Battery type and capacity significantly impact flight time and performance.
- Camera: Captures images and videos. Camera quality varies widely, impacting image resolution and other features.
- Transmitter: A remote control used to pilot the drone and adjust camera settings.
Drone Battery Types and Characteristics
Drone batteries are typically Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries, known for their high energy density. Different LiPo batteries have varying characteristics that impact flight time and performance.
- Capacity (mAh): Higher mAh indicates longer flight time.
- Voltage (V): Determines the power output of the battery.
- Cell Count (S): Indicates the number of cells in series within the battery pack, influencing voltage.
- Discharge Rate (C): Represents the maximum current the battery can safely deliver. A higher C rating is suitable for drones demanding high power.
Drone Propeller Types and Flight Performance
Propeller design significantly influences a drone’s flight characteristics. Different propeller designs offer trade-offs between thrust, efficiency, and noise levels.
- Slow-spinning propellers: Generally quieter and more efficient at lower speeds.
- Fast-spinning propellers: Produce more thrust but can be noisier and less efficient at lower speeds.
- Propeller size and pitch: Larger propellers generally produce more thrust, while pitch affects the efficiency and speed of the drone.
Common Drone Component Specifications
| Component | Weight (g) | Power Consumption (W) | Lifespan (hours/cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor (per motor) | ~20-50 | ~10-30 | Varies greatly depending on usage |
| Propeller (per propeller) | ~5-15 | N/A | Varies greatly depending on material and usage |
| Battery (typical) | ~200-500 | Varies greatly depending on load and battery capacity | 300-500 charge cycles |
| Flight Controller | ~20-50 | ~5-15 | Several years with proper care |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and successful drone operation. This ensures all systems are functioning correctly and reduces the risk of accidents.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive check to minimize risks and ensure smooth operation. This includes both technical and environmental checks.
- Battery Check: Verify battery charge level and condition. Inspect for any damage or swelling.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine propellers for cracks, damage, or loose attachment.
- Transmitter Calibration: Ensure the transmitter is properly calibrated and connected to the drone.
- GPS Signal Check: Confirm a strong GPS signal for accurate positioning and stability.
- Weather Conditions: Check for wind speed, precipitation, and visibility. Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Airspace Restrictions: Verify compliance with local regulations and airspace restrictions using apps like B4UFLY or similar.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone for any loose parts or damage.
Weather Conditions and Flight Safety

Wind speed and direction are critical factors. High winds can make controlling the drone challenging and potentially dangerous. Precipitation, such as rain or snow, can damage the drone’s electronics.
Legal Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Drone operation is subject to various regulations. These vary by country and region and often involve registration, licensing, and airspace restrictions. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules in your area.
Pre-Flight Checklist Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight checklist can aid in a methodical approach. This flowchart illustrates the sequential steps involved in the pre-flight process.
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here in a visual medium, but text-based representation is difficult. The steps above in the ordered list serve as a textual representation of the flowchart logic.)
Taking Off and Landing: How To Operate A Drone
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section Artikels the procedures for various environments and common mistakes to avoid.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The procedures for takeoff and landing may vary slightly depending on the environment and drone model. However, some general guidelines apply to most situations.
- Open Field: Choose a level, open area away from obstacles and people. Perform a slow, controlled ascent.
- Confined Space: Exercise extreme caution. Ensure ample clearance from obstacles. Use precise control and maneuver slowly.
Tips for Smooth Takeoffs and Landings
Smooth and controlled takeoffs and landings are essential for safety and preserving the drone’s condition.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a rewarding experience.
Remember to always prioritize safety when learning how to operate a drone.
- Gentle throttle control: Avoid sudden movements.
- Maintain visual contact: Always keep the drone within sight.
- Level surface: Land on a flat, stable surface.
- Slow descent: Lower the drone slowly to avoid damage.
Common Takeoff and Landing Mistakes
Several common mistakes can lead to accidents. Understanding these mistakes can help prevent them.
- Sudden throttle movements: Can lead to loss of control.
- Inadequate clearance: Can result in collisions.
- Landing in wind: Can cause the drone to drift or tip over.
- Ignoring warnings: Disregarding low battery warnings can lead to unexpected power loss.
Safety Precautions During Takeoff and Landing
Safety should always be the top priority. Here are some key precautions.
- Check surroundings: Ensure a clear and safe area before takeoff.
- Keep a safe distance: Maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles.
- Be aware of wind conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds.
- Monitor battery level: Land promptly when the battery is low.
Controlling the Drone in Flight
Understanding the basic controls is crucial for safe and effective flight. This section explains the controls and different flight modes.
Basic Drone Controls
Most drones use a control system based on four primary axes: throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw.
- Throttle: Controls the altitude (up and down).
- Pitch: Controls movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls movement left and right.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis (turning left or right).
Drone Maneuvering
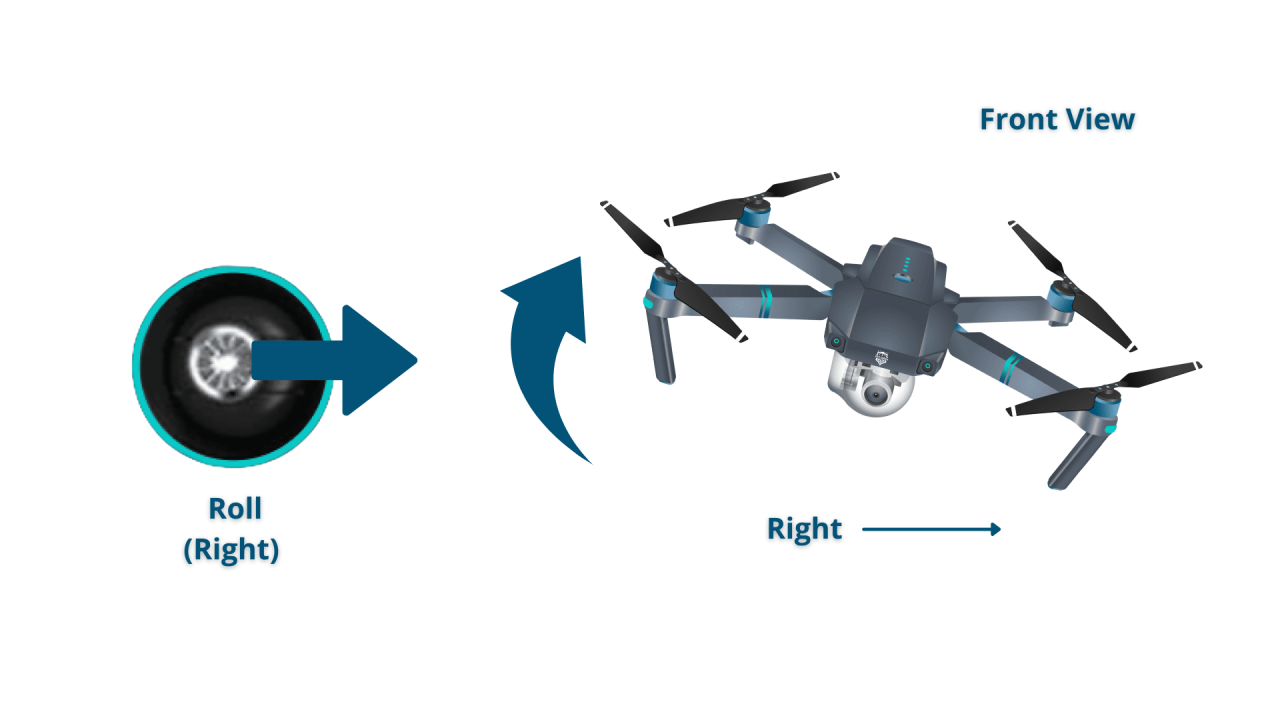
Combining the basic controls allows for precise maneuvering in all directions. Practice is key to mastering smooth and controlled flight.
- Hovering: Maintaining a steady position in the air.
- Forward Flight: Moving the drone forward.
- Sideways Flight: Moving the drone left or right.
- Turning: Rotating the drone left or right.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer different flight modes that assist with stability and control.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot’s perspective.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS signals for precise positioning and stability.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Here’s a step-by-step guide for performing some basic maneuvers.
- Hovering: Adjust the throttle to maintain a stable altitude.
- Forward Flight: Gently push the control stick forward while maintaining a steady throttle.
- Turning: Use the yaw control to rotate the drone smoothly.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
The camera is a key feature of many drones. Understanding the settings and techniques is vital for capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Drone Camera Settings
Drone cameras offer various settings to control image quality and capture style.
- Resolution: Determines the image size (e.g., 1080p, 4K).
- Frame Rate: The number of frames per second (fps), affecting video smoothness.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light, affecting image brightness and noise.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the lens, influencing depth of field.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Achieving high-quality results requires attention to detail and practice.
- Stable flight: Smooth camera movements are essential for crisp images and videos.
- Proper lighting: Avoid harsh shadows by shooting during the golden hour (sunrise or sunset).
- Appropriate settings: Adjust settings based on lighting conditions and desired results.
- Composition: Pay attention to the rule of thirds and leading lines for visually appealing shots.
Aerial Photography and Videography Composition Techniques
Effective composition enhances the visual impact of aerial footage.
- Rule of thirds: Place key elements off-center for a more balanced composition.
- Leading lines: Use lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry and patterns: Capture visually appealing symmetry and patterns from above.
Drone Camera Modes
Most drones offer various camera modes to simplify operation and capture specific effects.
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records video footage.
- Timelapse Mode: Creates a time-lapse sequence from a series of still images.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is crucial for maintaining functionality and avoiding costly repairs.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Several common issues can arise during drone operation.
- Low Battery: The most frequent problem. Always monitor battery levels.
- Motor Failure: A motor may fail due to damage or overheating.
- GPS Signal Loss: Can occur in areas with poor GPS reception.
- Connection Issues: Problems with the connection between the drone and the controller.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting steps vary depending on the specific problem.
- Low Battery: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor for damage and replace it if necessary.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception.
- Connection Issues: Check the controller’s batteries and ensure the connection is secure.
Common Error Messages
Drone controllers display error messages to indicate problems. Consult the drone’s manual for explanations of specific error codes.
Common Problems, Causes, and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t take off | Low battery, motor failure, GPS signal loss | Check battery, inspect motors, find a location with better GPS reception |
| Drone is unstable | High wind, low battery, faulty sensors | Avoid high winds, land the drone and recharge the battery, check sensors |
| Drone is drifting | Wind, GPS signal loss | Avoid high winds, find a location with better GPS reception |
| No signal | Low controller battery, interference | Replace controller batteries, move away from sources of interference |
Drone Safety and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation prioritizes safety and ethical considerations. This section Artikels best practices for safe and responsible drone use.
Maintaining Safe Distance
Always maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles to prevent accidents. Never fly over crowds or sensitive areas.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible operation involves respecting privacy, adhering to regulations, and avoiding reckless behavior.
Emergency Procedures

In case of an emergency, such as a malfunction or loss of control, follow these steps.
- Attempt to regain control: Try to recover control of the drone using standard procedures.
- Initiate RTH (if available): Use the return-to-home function if available.
- Land the drone safely: If possible, attempt a controlled landing.
- Report the incident: Report any incidents or accidents to relevant authorities.
Best Practices for Safe Drone Operation
Following best practices minimizes risks and ensures responsible operation.
- Always check weather conditions: Avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Never fly near airports or restricted airspace: Adhere to all regulations.
- Keep the drone within visual line of sight: Maintain visual contact at all times.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs: Impaired judgment can lead to accidents.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a solid foundation in both, covering the essential aspects of pre-flight preparation, flight control, safety procedures, and post-flight maintenance. By diligently following the steps Artikeld and prioritizing safety, you’ll be well-equipped to enjoy the exciting world of drone piloting responsibly and effectively. Remember to always check local regulations and fly safely!
FAQ Insights
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functionality, and a relatively simple control interface is recommended. Many readily available models fit this description.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s transmitter?
Calibrating your transmitter is generally recommended before each flight session to ensure accurate control. The frequency depends on your drone model and its usage, but regular calibration is good practice.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and attempt to regain the signal. If unsuccessful, carefully land the drone using manual control. Always prioritize a safe landing.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies significantly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15-30 minutes, but always check the manufacturer’s specifications.
